crwdns2935425:010crwdne2935425:0
crwdns2931653:010crwdne2931653:0





-
Let's take a deeper dive into the projector and waveguide optics.
-
So what's all this about six layers? There's a separate waveguide for each color channel (red, green, and blue) on two distinct focal planes.
-
Without color-specific waveguides, each color would focus to a slightly different point and deform the image.
-
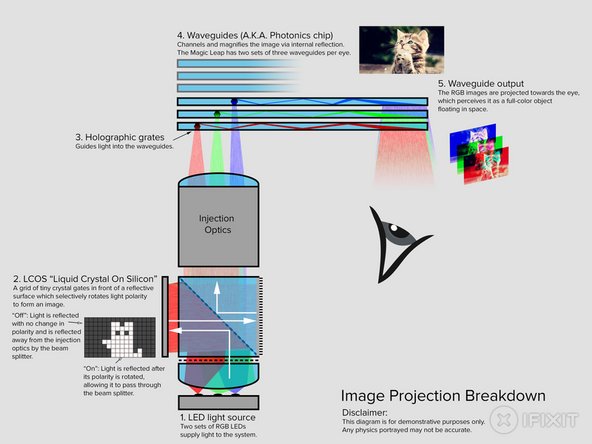
"Figure 6" from the Magic Leap patent application 2016/0327789 shines some light on the optics' inner workings.
-
For your edification and delight, we've included our own "tl;dr diagram" for this system, complete with cats.
crwdns2944171:0crwdnd2944171:0crwdnd2944171:0crwdnd2944171:0crwdne2944171:0